Remote Sensing and GIS Mapping
Remote sensing and GIS (Geographic Information System) mapping are complementary technologies used to collect, analyze, and visualize spatial data from the Earth’s surface. Remote sensing involves capturing data from satellites, drones, or aircraft using sensors that detect various wavelengths of light and energy, providing detailed information about land use, vegetation, water bodies, and urban development. GIS mapping then integrates this data with other spatial information, allowing for the analysis, management, and presentation of geographic data in layers. Together, these technologies enable accurate environmental monitoring, urban planning, disaster management, and resource management by offering a comprehensive view of geographical areas and their changes over time.

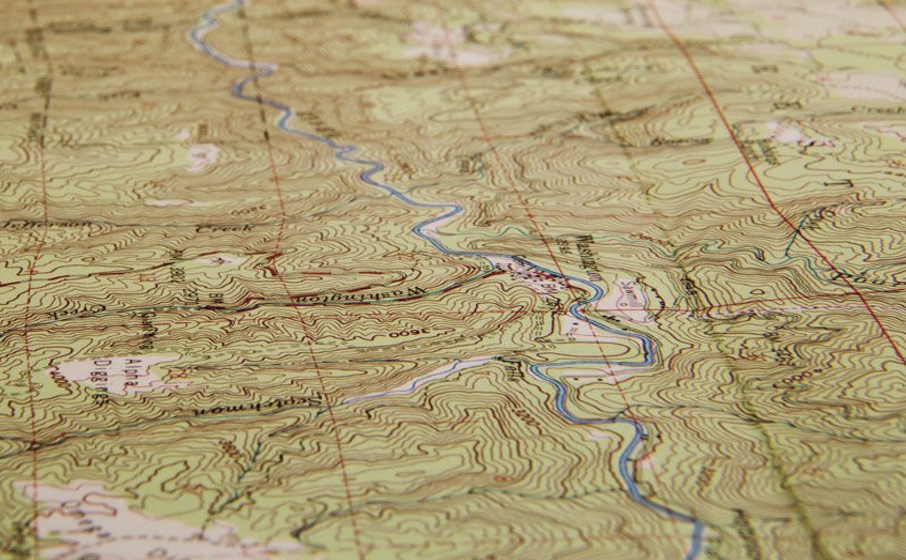
Topographic Map
A topographic map is a detailed representation of the Earth's surface that shows the shape and elevation of terrain features. It uses contour lines to depict changes in elevation and may include symbols and colors to indicate natural and human-made features such as rivers, roads, buildings, and vegetation. Topographic maps are essential tools for planning and engineering as they provide accurate spatial information for various purposes including land development, environmental management, navigation, and disaster planning. They enable users to visualize and analyze terrain characteristics, slopes, and drainage patterns, aiding in decision-making for infrastructure projects and resource management.
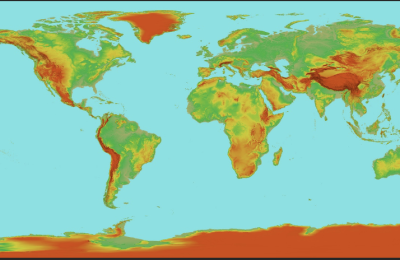
Digital Elevation Madel Map
A Digital Elevation Model (DEM) map is a digital representation of terrain elevation data in a specific geographic area. It uses a grid of elevation points to create a continuous surface, allowing visualization and analysis of terrain features such as hills, valleys, and slopes. DEM maps are generated using remote sensing technologies like LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) or photogrammetry, providing accurate three-dimensional representations of the Earth's surface. These maps are valuable for various applications, including hydrological modeling, flood risk assessment, landform analysis, and landscape planning. DEM maps support informed decision-making in environmental management, infrastructure design, and natural resource exploration by providing detailed elevation information across large geographic areas
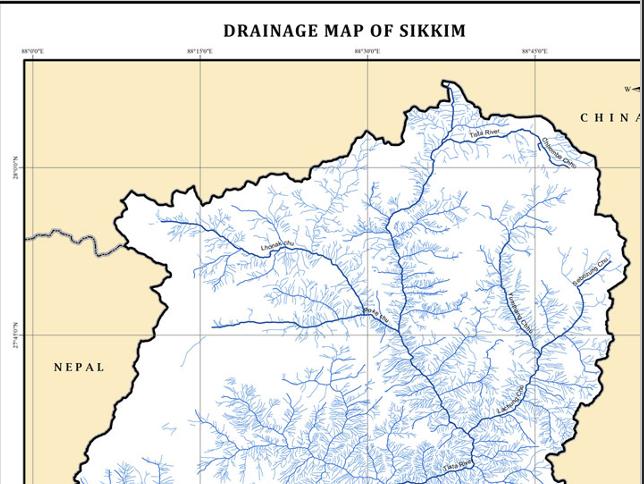
Drainage Map
drainage map is a specialized type of map that illustrates the natural or engineered drainage network within a geographic area. It typically depicts the flow of surface water, including rivers, streams, creeks, and their tributaries, as well as artificial drainage features like canals and drainage ditches. Drainage maps use symbols, lines, and colors to indicate the direction of water flow, watershed boundaries, and drainage basins. These maps are essential tools for water resource management, flood risk assessment, and environmental planning. They help identify drainage patterns, watershed boundaries, and potential flood-prone areas, aiding in the design of drainage systems and infrastructure to manage water resources effectively
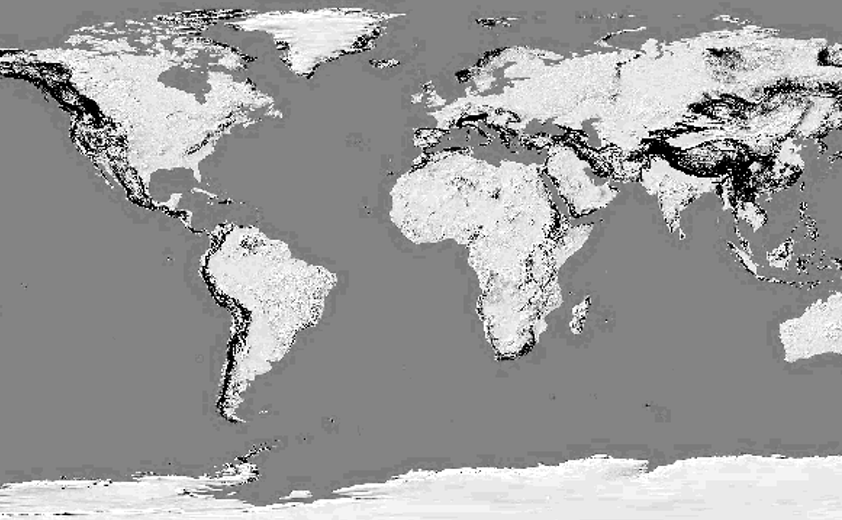
Hill Shade Map
A hillshade map is a type of topographic map that uses shading to visually represent the three-dimensional terrain of an area. It simulates the effects of sunlight on the landscape, creating shadows and highlights based on the elevation data of the terrain. Hillshade maps provide a realistic depiction of the terrain's shape and slope, enhancing the visualization of landforms such as hills, valleys, ridges, and mountains. These maps are widely used in cartography, land planning, and environmental analysis to aid in terrain visualization, landform interpretation, and decision-making for activities such as route planning, site selection, and landscape assessment.
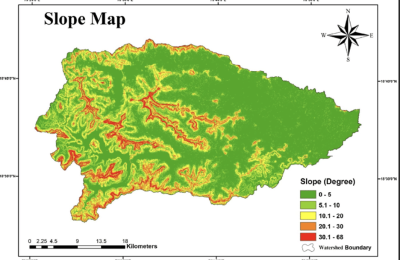
Slope Map
A slope map is a thematic map that illustrates the steepness or gradient of terrain surfaces within a geographic area. It uses color gradients or contour lines to represent the degree of slope, ranging from gentle slopes to steep inclines. Slope maps are derived from digital elevation models (DEMs) or topographic data, calculating slope values based on changes in elevation between adjacent points. These maps are valuable for various applications, including land use planning, engineering design, environmental assessment, and natural hazard management. They provide essential information for identifying areas prone to erosion, landslide risks, and determining suitable locations for infrastructure development and land management practices.
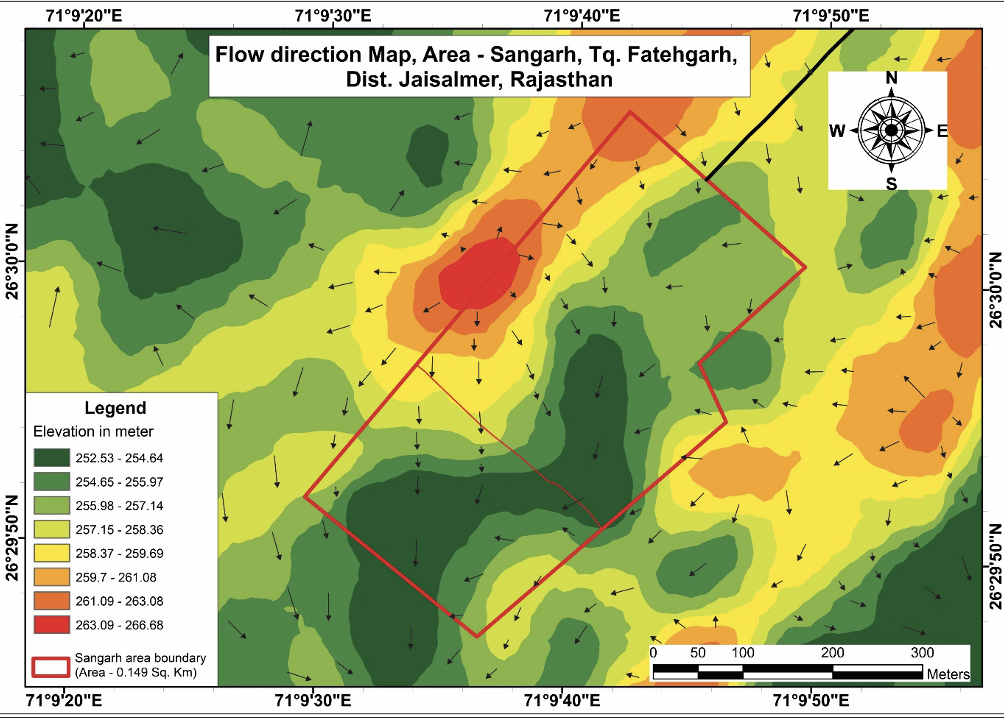
Flow Map
A flow map is a type of thematic map that visualizes the movement or direction of phenomena, such as transportation routes, migration patterns, or natural processes like water flow. It uses arrows, lines, or gradient colors to represent the direction and magnitude of movement between locations or regions. Flow maps are useful for analyzing spatial relationships, understanding connectivity, and identifying patterns in the movement of goods, people, or resources. They are applied in various fields including transportation planning, urban development, epidemiology, and environmental studies to facilitate decision-making and spatial analysis based on movement dynamics and connectivity between locations.
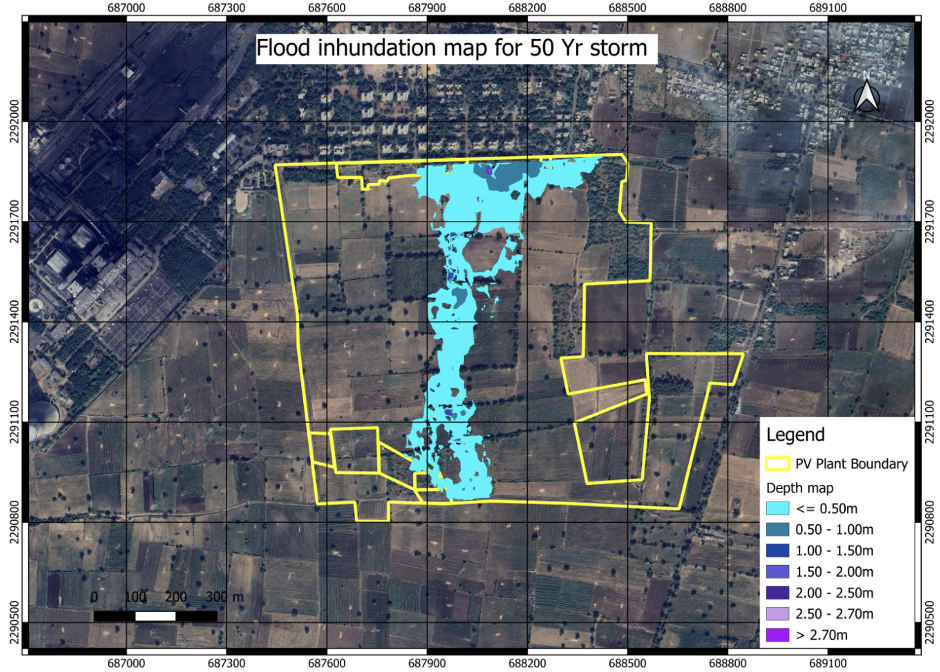
Flood Instrumental Model
A flood Inundation model is a numerical or computer-based simulation that predicts the extent and depth of flooding in a specific area under different scenarios. It integrates data such as topography, land use, rainfall patterns, and river flow rates to simulate how water would spread across the landscape during a flood event. Flood inundation models typically generate maps showing areas likely to be inundated, helping emergency responders, planners, and communities prepare for and mitigate flood risks. These models are crucial for flood risk assessment, disaster management, land-use planning, and infrastructure design to enhance resilience and reduce the impact of flooding on communities and the environment.
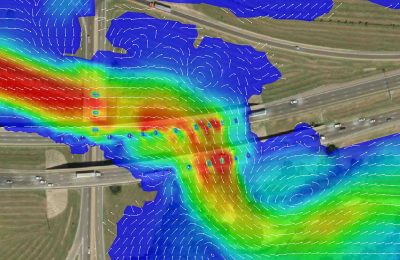
Hydrallic Modelling
Hydraulic modeling is the simulation of water flow through natural or constructed systems using mathematical models. These models help engineers understand how water behaves under different conditions, allowing for effective design, analysis, and management of water-related infrastructure such as rivers, lakes, reservoirs, stormwater systems, and sewage networks.
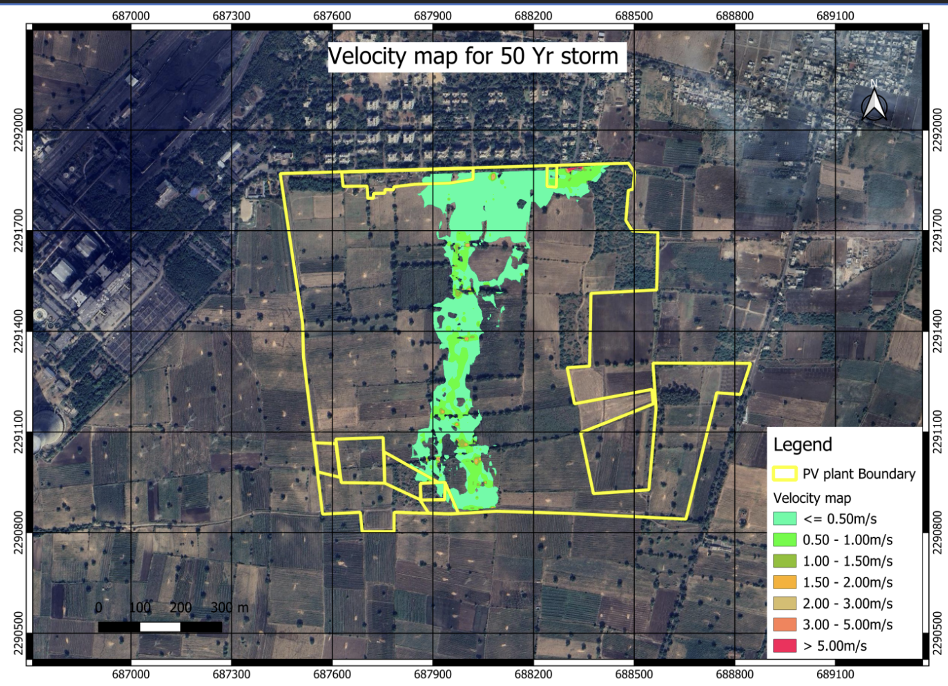
Flood Velocity Model
A flood velocity model is a specialized simulation that predicts the speed and direction of water flow during a flood event in a particular area. It uses hydraulic principles and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) techniques to simulate the movement of water through channels, rivers, or urban drainage systems. By integrating data such as topography, rainfall intensity, and river characteristics, flood velocity models calculate the velocity of water at different points within the floodplain. These models generate maps or visualizations showing variations in flow velocity, helping to assess flood hazards, identify areas at risk of fast-moving water, and inform evacuation plans and flood management strategies. Flood velocity models are essential tools for flood risk assessment, infrastructure design, and emergency response planning to mitigate the impact of floods on communities and infrastructure.
Land Use and Land Cover Map
Land use and land cover refer to the physical and functional characteristics of land within a geographic area, typically depicted on thematic maps. Land use describes how land is utilized by humans for various purposes such as residential, commercial, industrial, agricultural, recreational, or conservation activities. It indicates the economic and social activities taking place on the land and is crucial for urban planning, resource management, and environmental conservation. Land cover, on the other hand, refers to the physical coverage of the Earth's surface by vegetation, water bodies, bare soil, or artificial structures like buildings and roads. It provides information about the natural and artificial features priisent on the land and is essential for ecological studies, habitat mapping, and assessing changes in environmental conditions over time. Together, land use and land cover maps provide valuable insights into the spatial distribution and dynamics of human activities and natural resources within a region, supporting sustainable development, natural resource management, and environmental monitoring efforts
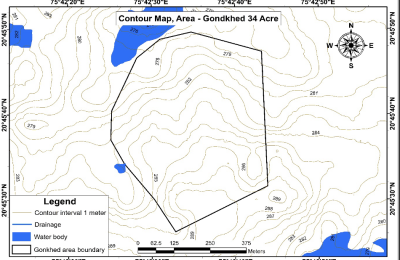
Counter Map
A contour map, also known as a topographic map, is a type of map that represents the three-dimensional shape and elevation of the Earth's surface using contour lines. Contour lines connect points of equal elevation, showing the height above sea level of different features such as hills, valleys, mountains, and plainst The spacing between contour lines indicates the steepness of slopes: closely spaced lines represent steep slopes, while widely spaced lines indicate gentle slopes. Contour maps are essential tools in geology, geography, land planning, and engineering. They provide detailed information about terrain features, landforms, and elevation
