Field Test
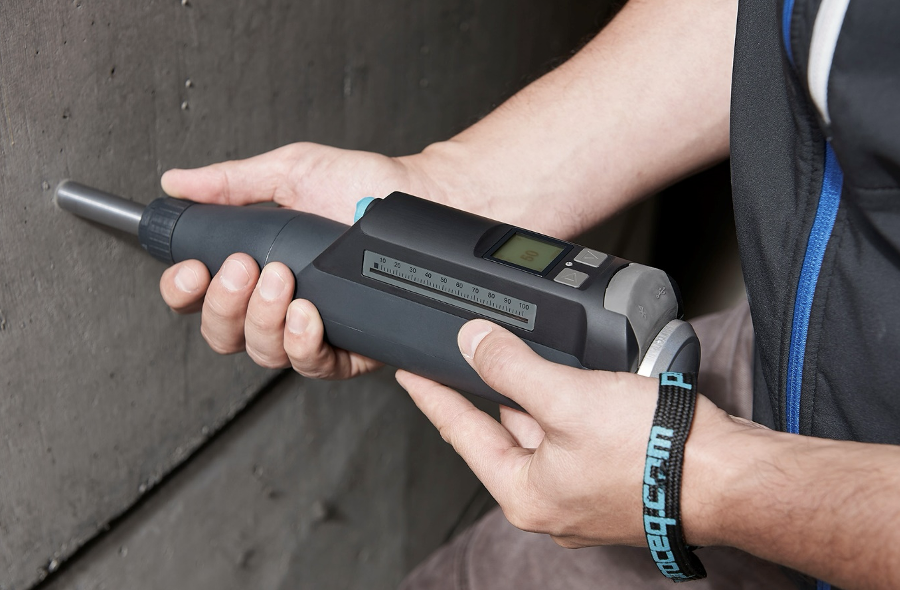

Filed test description updated for land survey change it to: Field tests in geotechnical investigations are on-site procedures conducted to assess the physical and mechanical properties of soil and rock. These tests provide critical data for evaluating the suitability of a site for construction and for understanding subsurface conditions that might affect the stability and safety of proposed structures. Common field tests include the Standard Penetration Test (SPT), which measures soil resistance to penetration; Cone Penetration Testing (CPT), which evaluates soil stratification and strength; and vane shear tests, which determine the shear strength of soft clays. Additionally, in-situ density tests, such as the sand cone or nuclear density gauge, are used to assess the compaction quality of soil layers. These tests help engineers make informed decisions about foundation design, slope stability, and earthworks.

Pile Load Test
Pile Load Testing is essential for evaluating the load-bearing capacity of deep foundations like piles or drilled shafts. This test involves applying a controlled load to the pile and measuring the resulting settlement to assess its performance under stress. By verifying design assumptions and confirming the foundation's ability to support intended loads, Pile Load Testing ensures structural integrity and safety in construction projects reliant on deep foundations.

Soil Permiability Test
A soil permeability test measures the rate at which water flows through soil, which is critical for understanding drainage, groundwater movement, and soil stability. It helps in assessing the suitability of soil for construction projects like foundations, retaining walls, embankments, and landfills.

Non Destructive Rebound Hummer Test
Non-destructive testing (NDT) encompasses a variety of techniques used to assess the properties of materials and structures without causing damage. In construction, NDT methods like ultrasonic testing, Rebound hammer testing, and Half-cell potentiometer tests are employed to evaluate the condition of existing structures, detect flaws, and ensure structural safety and reliability. One specific NDT method, the Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Test, measures the speed of ultrasonic pulses through concrete to assess its quality and integrity. This test helps identify voids, cracks, or other anomalies, making it invaluable for evaluating the structural health of concrete elements and ensuring their long-term durability.

Plate Load Test
The Plate Load Test is a crucial method used to ascertain the bearing capacity of soil, particularly for foundation design purposes. In this test, a steel plate of known diameter is placed on the ground, and a load is incrementally applied. Engineers measure the settlement of the plate at different load levels to gauge the soil's ability to bear loads and support structures effectively. This test provides essential data that informs decisions regarding foundation design, ensuring structures are supported safely and efficiently on the underlying soil.

Concrete Core Testing
Concrete core testing involves extracting cylindrical cores from hardened concrete structures for testing purposes. These cores are analyzed to assess compressive strength, evaluate concrete quality, and identify defects or deterioration within the structure. This testing is critical for evaluating the structural integrity of existing concrete elements and ensuring they meet safety and performance standards. By providing detailed insights into the condition of concrete, core testing informs decisions on maintenance, repairs, and structural enhancements to prolong the service life of concrete structures
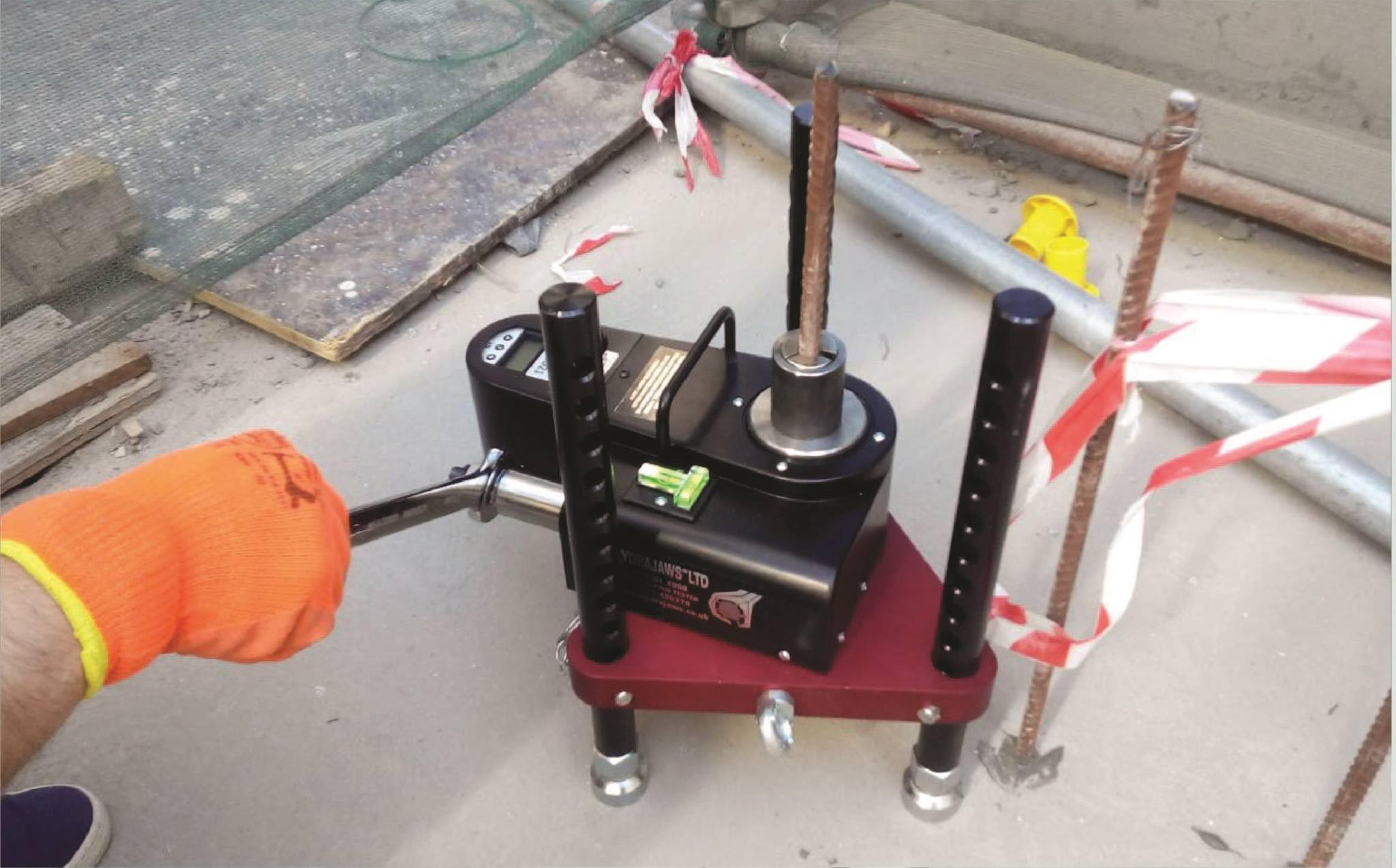

Pull Out Test
The Pull-Out Test is a method used to evaluate the bond strength between concrete and embedded reinforcement or anchors. In this test, a force is applied to pull an embedded object (such as a rebar or anchor) from the concrete, and the resistance to this force is measured. It helps assess the effectiveness of concrete bonding and the structural integrity of connections, ensuring they meet design specifications and safety standards in construction projects.
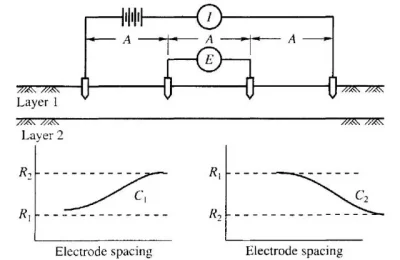
Electrical Resistivity Test
Electrical Resistivity Test (ERT) is a non- destructive technique used to measure the electrical resistivity of soil, rock or concrete. By passing an electrical current through the material and measuring the resulting voltage, ERT assesses the material's ability to conduct electricity. This test provides valuable information about the moisture content, compaction, and corrosion potential of soil or the quality and durability of concrete structures. ERT is particularly useful for evaluating subsurface conditions, assessing the integrity of foundations, and determining the effectiveness of corrosion protection measures in infrastructure projects.

Pressure Meter Test
Pressure Meter Test, also known as the Permeability Test, is a method used to assess the permeability of soil. It involves inserting a cylindrical probe into the ground and applying pressure to the soil. By meas g the volume change and pressure response, engineers determine the soil's permeability, which indicates how easily water can flow through it. This test is crucial for evaluating soil conditions and designing effective drainage systems, foundations, and earthworks in construction and geotechnical engineering projects
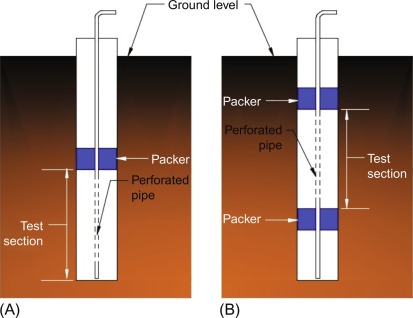
Packer Test
The packer test, also known as the Lugeon test, is an in-situ permeability test conducted in boreholes to assess the hydraulic conductivity of rock formations. It is widely used in geotechnical and hydrogeological investigations, especially for dam foundations, tunnels, and other subsurface projects.

Soil Thermal Resistivity Test
The soil thermal resistivity test measures the ability of soil to resist heat transfer. It is critical for designing underground electrical cables, pipelines, and thermal energy storage systems to ensure efficient heat dissipation and prevent overheating or damage to infrastructure.
